Pollution Control Systems
_______________________________________________________
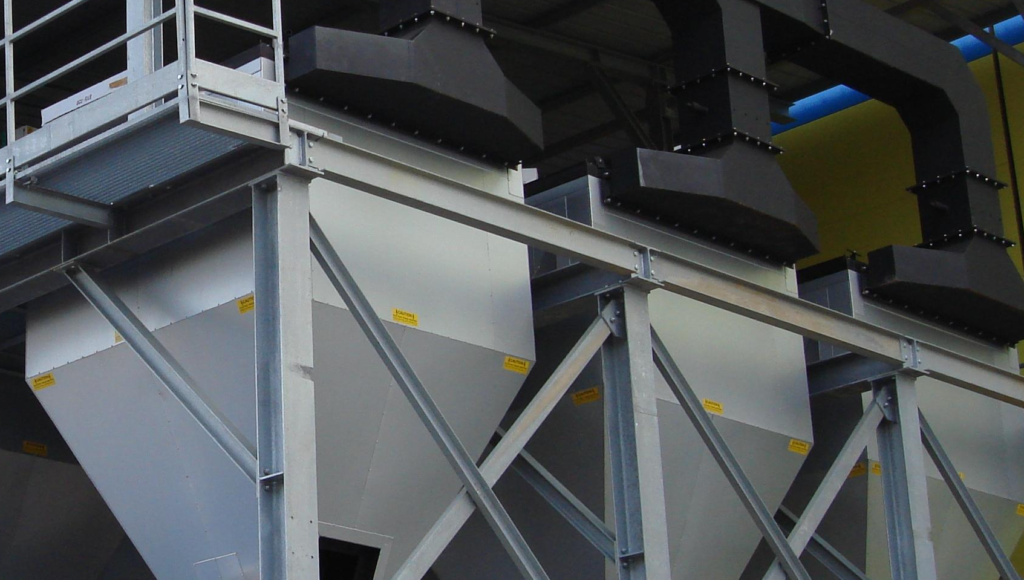
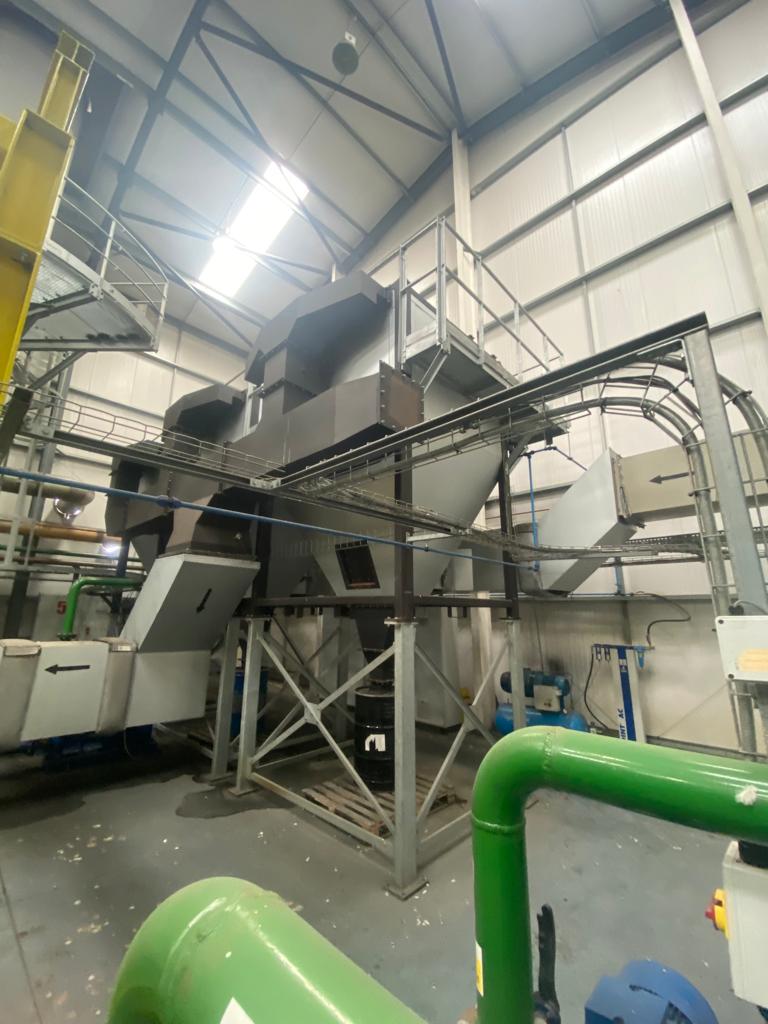
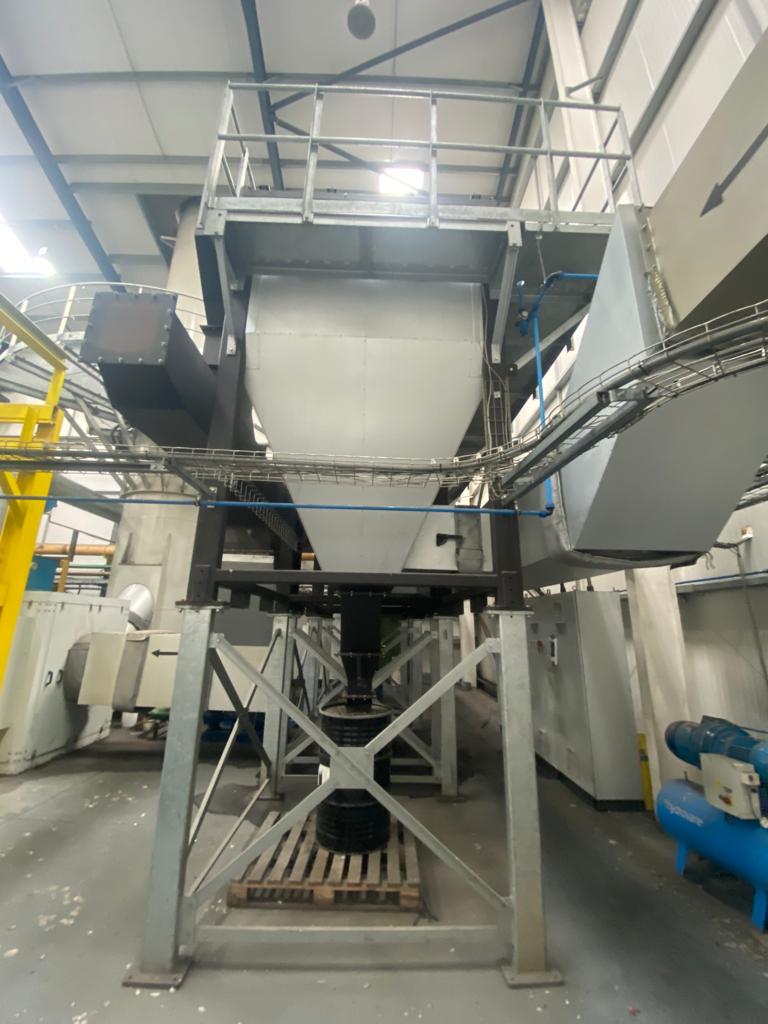
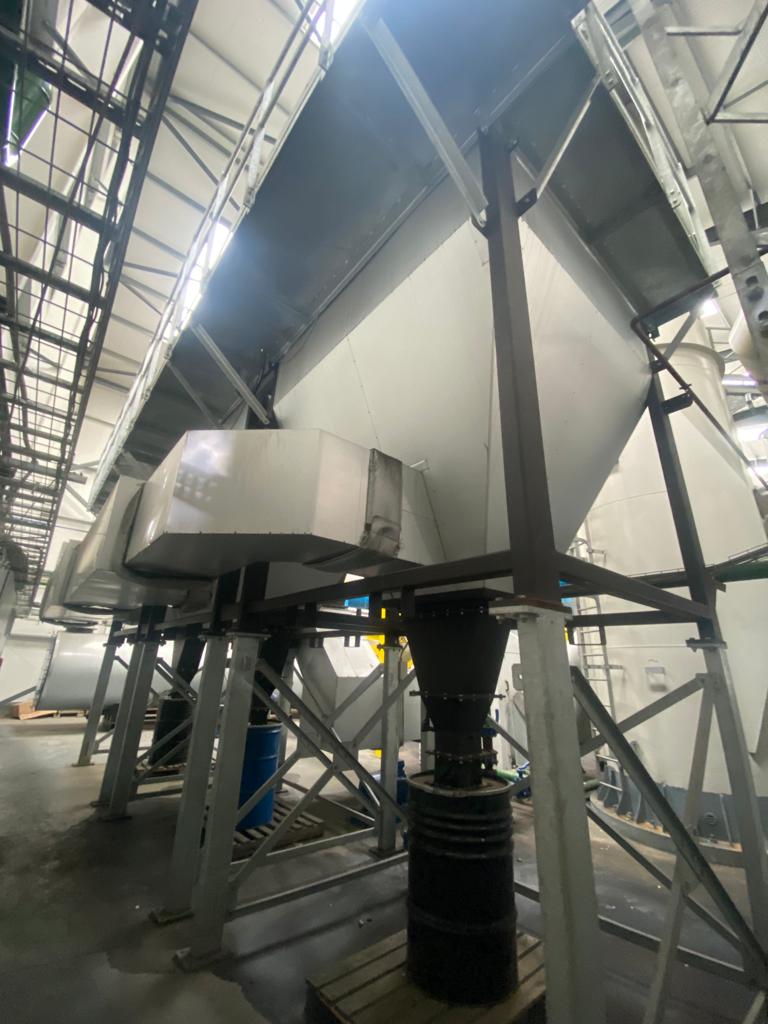
AIC Group offer a range of pollution control systems to suit a wide variety of applications offering an extremely high level of gas cleaning efficiency, compact equipment footprint as well as low running costs versus wet filtration systems.
Unlike conventional bag filters and other types of filtration, ceramic filters are highly efficient. They have the ability to remove submicron particles as small as a nanogram.
In operation they do not flex which prevents submicron particles from entering the substrate.
All systems are fully controllable via touchscreen HDMI.
How it all works:
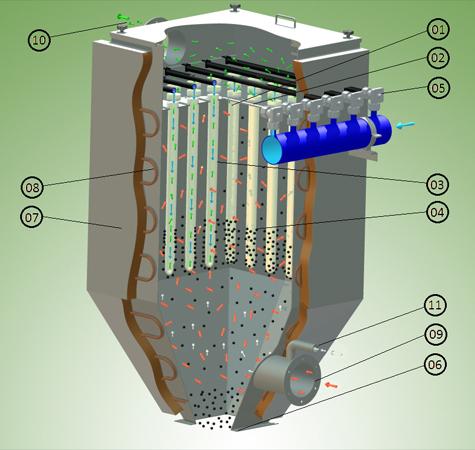
- The Element (1) hangs vertically from header plate (2) within the filter vessel. The header plate separates the filter’s clean and dirty compartments.
- Hot Gas is drawn through the filter medium (3) from outside to inside.
- Particulates and dry scrubbing sorbents are collected on the outer surface (4) of each filter element. These consist of the PM10, PM2.5 size ranges; these agglomerate.
- The particles are removed from the element by reverse jet cleaning (5). This reversal causes the accumulated solids to be detached from the outer surface of the ceramic filter elements.
- The particulates and spent dry-scrubbing sorbents are discharged through the hopper outlet (6) for collection and disposal.
- The filter body can be protected with insulation (7) and trace heated (8) to prevent the formation of the condensation when the equipment is not in use.
- Incoming gas stream (9) and sorbent (if required).
- Outgoing cleansed gas stream (10)
- Injection point for activated carbon and/or sodium bicarbonate (11)
Typical emissions with the use of sodium bicarbonate and activated carbon are as follows:
| Particulate | < 3mg/Nm3 (typically 1) | SO2 | < 50mg/Nm3 |
| HCl | < 10mg/Nm3 | HF | < 1mg/Nm3 |
| NOx | < 200mg/Nm3 | Heavy Metals | < 0.5mg/Nm3 |
| Dioxins | < 0.1ng/Nm3 |
Typical particulate emissions of other types of filters:
| Bag filter | 7 to 10mg/Nm3 | Cyclone | > 10mg/Nm3 |
Make an Enquiry
Simply fill out the short form below for more information

 +44 (0)28 3752 6157
+44 (0)28 3752 6157 info@aic-group.co.uk
info@aic-group.co.uk